
Table of Contents
Subdomain vs addon domain are both ways to organize and manage multiple websites within a single hosting account, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Here’s a comparison between subdomains vs addon domain.
A Subdomain is an extension of your main domain. If your site is example.com, then you could create a Subdomain like foo.example.com. This domain does not need to be registered and is not treated as a separate site. An Addon Domain is a separate domain with its own unique content and own Domain Name
Subdomain and it’s features:
- Definition: A subdomain is a prefix added to a domain name, creating a new address within the same domain. It appears as “subdomain.maindomain.com.”
- Purpose: Subdomains are typically used to organize and categorize different sections or areas of a website. They allow you to create separate websites, applications, or sections within the same domain.
- Technical Implementation: Setting up a subdomain involves creating a DNS record that points to a specific directory or location on your web server. Each subdomain can have its own content, settings, and functionality.
- Example Use Cases:
- Blog: blog.example.com
- Store: store.example.com
- Support: support.example.com
- Resource Sharing: Subdomains share the resources (disk space, bandwidth, etc.) of the main domain and hosting account. They do not require additional hosting plans.
Subdomain vs Addon Domain difference:
Addon Domain and it’s features:
- Definition: An addon domain is a separate domain name that is added to an existing hosting account, creating a new website with its own directory and content. It appears as “adddondomain.com.”
- Purpose: Addon domains are used to host multiple independent websites within the same hosting account. Each addon domain functions as a separate website with its own content, settings, and domain name.
- Technical Implementation: Adding an addon domain involves configuring DNS settings and creating a new directory on the server to host the website files. Each addon domain has its own document root and operates independently of other domains.
- Example Use Cases:
- Multiple websites for different businesses or projects.
- Creating additional websites for clients or customers.
- Experimenting with different website ideas or niche markets.
- Resource Allocation: Addon domains have separate resource allocations (disk space, bandwidth, etc.) from the main domain and hosting account. They may require additional hosting plans or upgrades depending on the hosting provider’s policies.
- Brand Identity: Addon domains allow you to create separate websites with unique domain names, which can help establish distinct brand identities and target different audiences. Each addon domain can have its own branding, design, and messaging.
Subdomain vs Addon Domain:
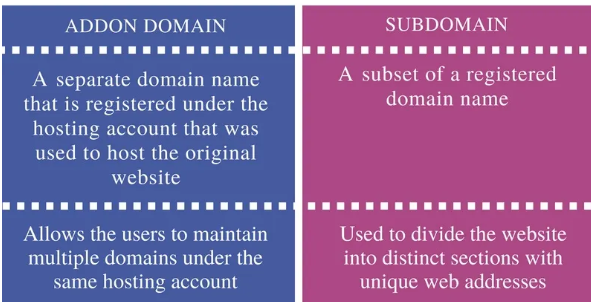
Addon domain is a separate domain name that is registered under the hosting account that was used to host the original website. Subdomain is a subset of a registered domain name.
Conclusion:
A domain name is a string that allows identifying an organization in the WWW. Addon and subdomain are two types of domains. The difference between Addon Domain and Subdomain is that the Addon domain is a domain that is added into the user’s hosting account which was used to host his original domain while the subdomain is a subpart that is directly related to the user’s original domain.
In summary, subdomains are used to create separate sections or areas within a single domain, while addon domains are used to host multiple independent websites within the same hosting account. The choice between subdomains and addon domains depends on your specific needs, such as organization, resource allocation, and website management.
